The Evolution of Decentralized Finance
Jan. 20, 2025

Millions of DeFi Users in Europe
The EBA (European Banking Authority) and ESMA (European Securities and Markets Authority) released a joint report on recent developments in crypto-assets, commissioned by the European Commission. With a significant focus on Decentralized Finance (DeFi), European authorities gathered new data through an NCA (National Competent Authority) survey to identify ecosystem actors, market shares, and DeFi usage.
The market for DeFi remains a niche globally, accounting for just 4% of the total crypto-asset market capitalization as of late 2024. The EU shows higher-than-average global adoption but lags behind countries like the United States and South Korea. Approximately 7.2 million DeFi users exist in Europe, but only 15% engage with DeFi protocols on a monthly basis.
Institutions Developing Interest in DeFi
Based on the EBA's Risk Assessment Questionnaire, only 5% of European banks currently engage in crypto-related activities, primarily custody services. However, this number is expected to double within the next two years, with 10% of EU banks planning to engage in crypto activities, including the reception and transmission of orders.
In DeFi specifically, 1% of banks are active, while 7% are exploring, testing, or planning deployment. Meanwhile, EU investment funds remain minimally exposed to crypto-assets, representing just 0.02% of total assets under management.
Observed Usage of Decentralized Finance
The DeFi ecosystem desmonstrates diverse applications, with usage patterns evolving over the years:
- Liquidity Provision (LP) for Swaps: LPs, historically central to decentralized finance, LP activity has shrunk to 8% of total DeFi usage, partially due to a broader range of crypto-asset offerings on centralized exchanges.
- Staking Activities: Blockchain transitions like Ethereum's move to Proof of Stake (PoS) have propelled staking to dominate 39% of DeFi activity, driven by crypto-native yields and liquid staking protocols.
- Lending and Borrowing: Decentralized lending protocols offer innovative financial instruments. Yield generation through over-collateralized lending pools provides a safer alternative compared to direct lending models targeting large digital asset players.
On DeFi Lending and Borrowing
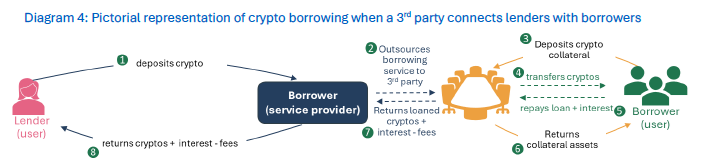
Crypto lending relies on over-collateralization where customers place crypto-assets or funds as collateral in an account held at the service provider to obtain the loan. The collateral value is usually higher than the loan amount.
"The report finds that centralised crypto lending offers loan-to-value ratios between 20-80%, with liquidation thresholds typically at around 85%. The report finds that interest rates paid by borrowers typically range between 8 to 15% but finds evidence of rates offered at a higher level."
DeFi protocols offering lending and borrowing services typically rely on liquidity pools (peer-to-pool lending), which dynamically match demand and supply using a flexible interest rate model designed to optimize fund utilization within the pool.
These pools generate revenue through a narrow interest rate spread while offering additional protection and revenue streams, such as liquidation fees, incentives in governance tokens, and market-making fees.
Liquidity pools are the most popular applications in lending and borrowing, though other lending models include:
- Collateralized Debt Position (CDP): The user borrows directly from the DeFi application.
- Collateralized Debt Market (CDM): The user borrows funds deposited by lenders in a DeFi application.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P): Individual loan requests are posted on a platform, and lenders and borrowers are matched based on their constraints and preferences.
Transparency as an Advantage for Supervision
DeFi's borderless nature presents regulatory challenges, as activities often fall outside jurisdictional boundaries. CASPs under the EU’s AMLD provisions must enforce Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing measures, including on DeFi-related services. However, unregulated service providers create an uneven playing field.
The report also emphasizes embedded supervision - leveraging blockchain’s transparency to monitor activity in real-time and identify key risk indicators. This approach requires technical expertise to map DeFi protocols, understand their technical operations, and integrate automated oversight mechanisms.
Smart contract audits could be a pathway explored by regulators to enhance trust and security within the ecosystem and protect consumers.
Perspectives: Market risk
System-wide market risks arise from the procyclicality of crypto assets and the rehypothecation of collateral. One leveraged risk highlighted is liquid restaking, where a de-peg can trigger liquidations across the collateral chain.
Regarding systemic market risks, due to over-collateralization requirements and subject to market conditions, the liquidation of assets held as collateral may ensure that lenders do not suffer losses. However, the activation of liquidation introduces risks to borrowers, with the rigidity of smart contract operations further amplifying procyclicality under stress conditions.
The Need for Financial Education
Raising public awareness about usage in DeFi is essential. Economic benefits, yield generation mechanisms and risks are often buried in technical and legal language that demands advanced literacy.
While blockchain promises financial inclusion, this potential is hindered by the challenges of understanding complex protocols, economic rationales, and opaque risk profiles. To bridge this gap, financial education must simplify these concepts, empower users, and open access for a safer participation in DeFi.
Follow our media and our social networks (LinkedIn) for accessible, insightful and educational content to help you navigate the decentralized finance ecosystem with confidence.